Crop Protection Division
Introduction:
The main thrust of research is to reduce the crop yield losses by management of diseases and insect-pests. Moreover, emphasis is on development of eco-friendly and sound methods for crop management and enhancing livelihood security of farmers through adoption of secondary agriculture viz. mushroom cultivation and apiary.
Major activities:
- Survey and surveillance of crop diseases and insect – pests.
- Screening of genetic stocks under epiphytotic conditions for identification of resistant sources.
- Evaluation of breeding materials for varietal development.
- Ecofriendly management of diseases and insect-pests.
- Livelihood security through secondary agriculture.
Patents Granted
1. Patent: IN290170 The VL Whitegrub beetle trap on 30.11.2017
-
The uniqueness of the trap is space between the light source and the hitting fins and the gap between the funnel stem and the collection pot.
-
Allows the beneficial insects being weak fliers and attracted towards light to pass on and not getting hit and trapped.
-
The trap is found to capture 68% of scarab beetles, 32% others (mostly of Isoptera and Lepidoptera) and <0.8% of beneficial insects.
-
A trap normally capture around 10,200 beetles per season (June to October) in the first year of installation at a site and around 5,000 beetles in the second year at the same place which reduce to 800 in the fifth to sixth year.

2. A process for the mass production of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) biocide using millet grain based agro-medium
- The invention discloses a process for preparation of biocide using a cold tolerant/environmentally competitive and highly entomopathogenic isolate (strain VLBt 6) of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. galleriae/colmeri (MTCC 8997) isolated from the North-Western Himalaya.
- The strain is highly entomopathogenic and capable of producing larger quantity of delta-endotoxin (crystal toxin) with broad range as well as enhanced pesticidal/insecticidal activity.
- It is found highly insecticidal against diamondback moth Plutella xylostella, cabbage butterfly Pieris brassicae, cabbage semiloopers Thysanoplusia ni and T. orichalcea, cabbage leaf webber Crocidolomia binotalis, amaranth leaf webber Hymenia recurvalis and tomato fruit borer Helicoverpa armigera etc.
- The biocide is found quite toxic to the specific target insects, but is harmless to plants and other non-targeted organisms. Furthermore, it is cold tolerant and thus tends to sporulate even at low temperature.
Technologies Commercialized
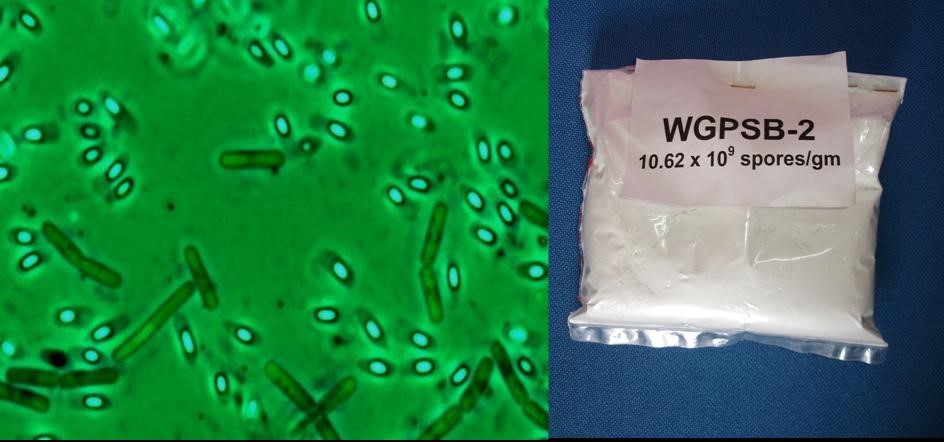
- Bacterial entomo-pathogen based formulation (Bacillus cereus - WGPSB2)
The bio-agent, Bacillus cereus strain WGPSB2 is effective for the management of white grubs. Bacillus cereus WGPSB2 is a gram +ve bacteria isolated from diseased white grubs, formulated in talc for field applications. It cause disease to the grubs when ingested by the early stage of grub and kills them. It is found effective to the grubs but safer to other native microbes in soil and not hazardous to other living organisms. It is an effective alternative for chemical pesticides which are used for the management of white grubs in the region.
2. Whitegrub beetle trap -1
The whitegrub beetle trap is a light based insect trapping device used to attract and capture whitegrub beetles. Whitegrubs beetle trap is efficient, cost effective, light weight and user friendly light based insect trap specific for capturing whitegrub beetles. It consists of a CFL assembly, hitting fins, funnel, and collection pot designed to attract and capture white grub beetles. It is found very effective for monitoring and mass trapping of white grub beetles.

3. Trichoderma harzianum strain 28, bio-pesticide against soil-borne fungal pathogens
This isolate (Tr-28) possesses broad-spectrum activity against diverse soil-borne plant pathogens. The isolate Tr-28 showed high antagonistic activity in vitro against six major soil borne plant pathogens viz., Rhizoctonia solani, Sclerotium rolfsii, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Fusarium solani, Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lentis and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi. Under field studies, it was found promising in reducing many soil borne diseases viz. wilt and root rot of garden pea and lentil, root rot of french bean, damping off of tomato, capsicum and cauliflower. The isolate additionally possess plant growth promoting activity and also tolerant to cold.
Major Research Areas:
Disease Scenario
- Blast and brown leaf spot in rice, Turcicum leaf blight and Banded leaf and sheath blight in maize, blast in finger millet, yellow and brown rusts in wheat are the important diseases in cereals.
|
Leaf blast of rice |
Neck blast of rice |
Turcicum leaf blight of maize |
|
Blast of finger millet |
Banded leaf & sheath blight of maize |
Yellow rust of wheat |
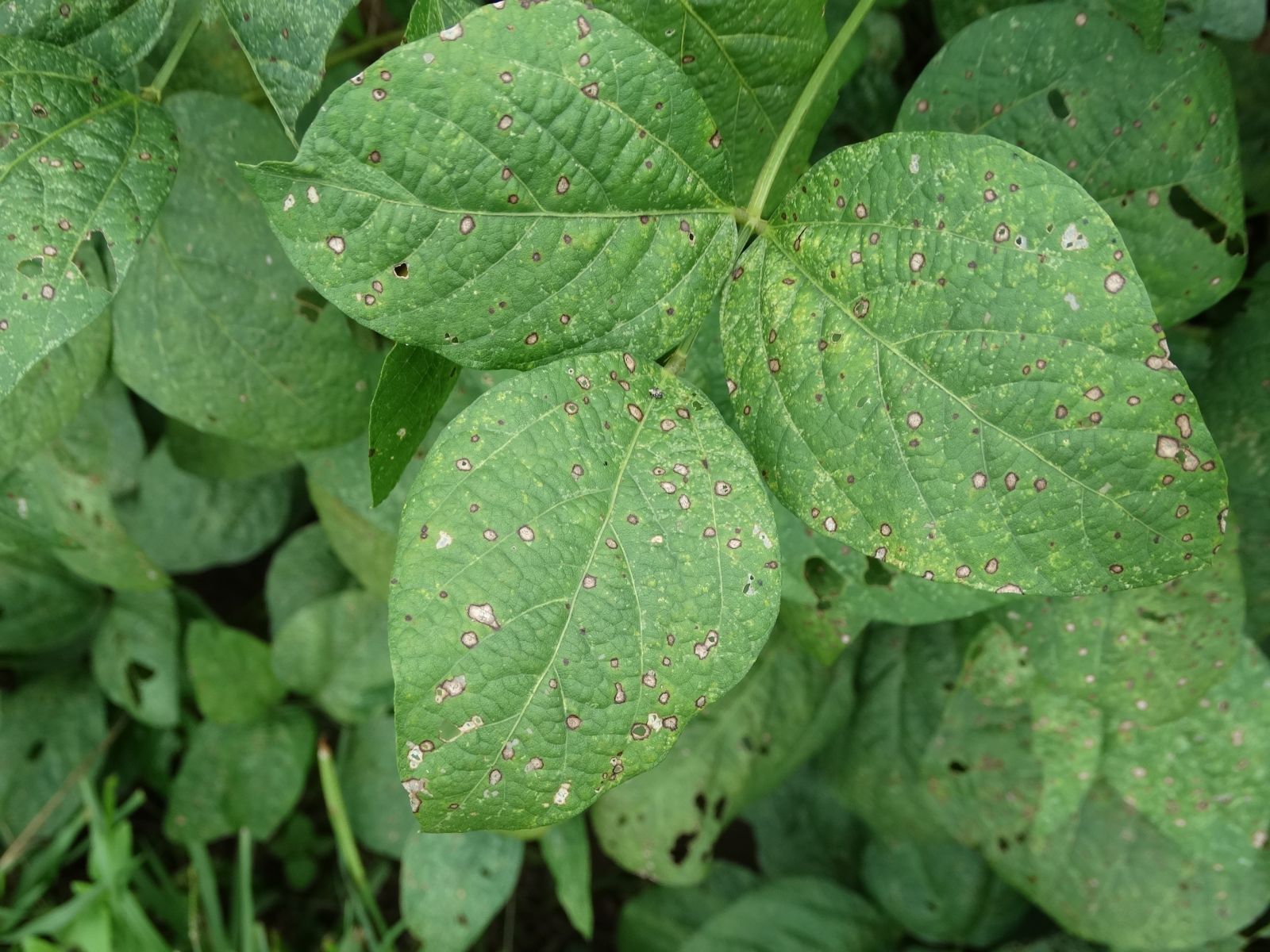
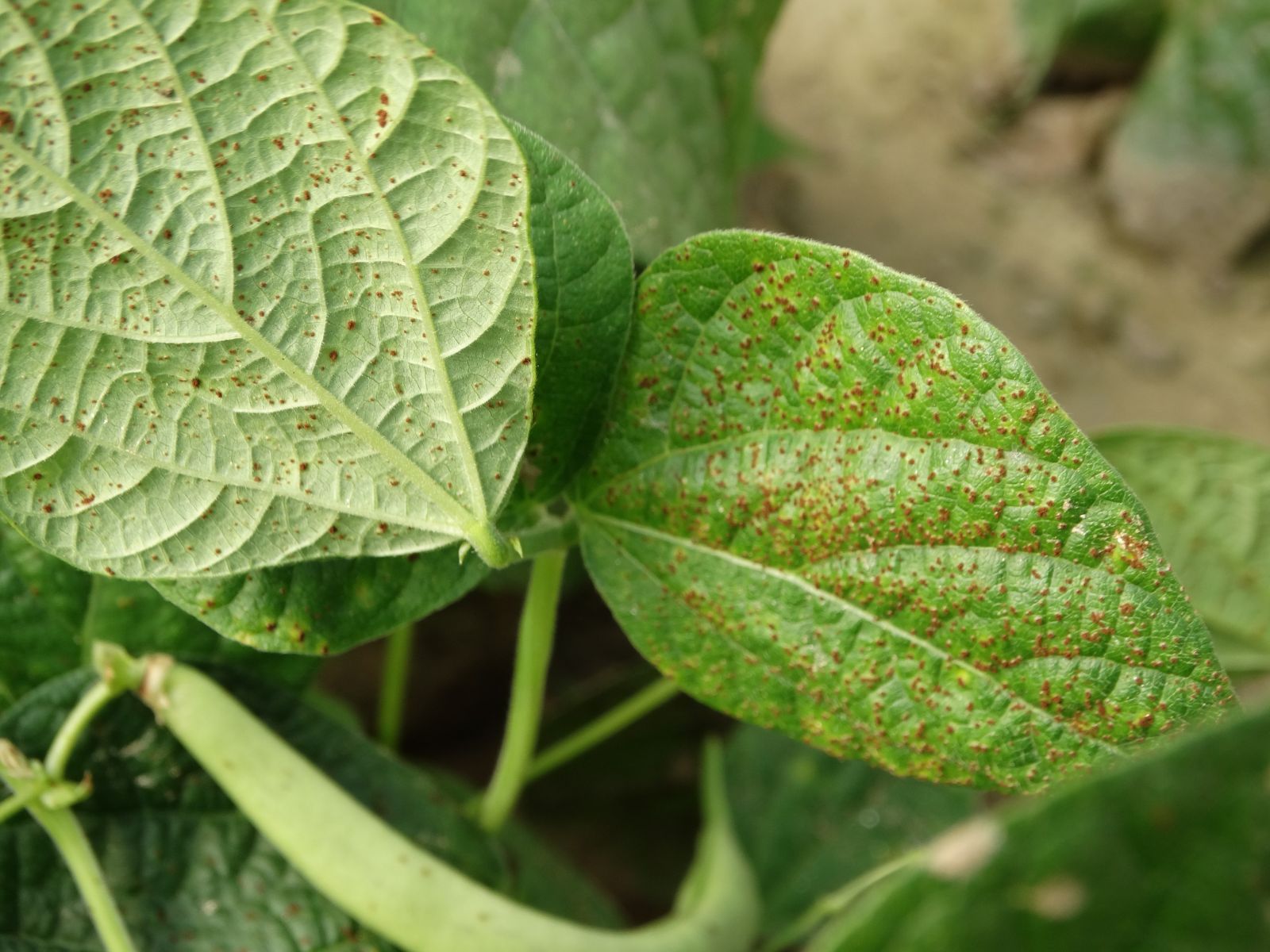
- In pulses and oilseeds, frogeye leaf spot of soybean, wilt of lentil are severe and anthracnose in horse gram appears in moderate intensitie
|
Frog eye leaf spot of soybean |
Wilt of lentil |
Wilt of pigeon pea |
Purple blotch in onion and garlic, early blight, bacterial wilt, buckeye rot in tomato, powdery mildew and wilt in pea, root rot and black rot in cauliflower, angular leaf spot and rust in French bean, bacterial wilt, powdery mildew and anthracnose in capsicum are important diseases of vegetables.
|
Purple blotch of onion |
Rust of french bean |
Angular leaf spot of bean |
Insect-pests Scenario
- White grub, a polyphagous pest, which devastates almost all the kharif crops, is the most menacing insect of the region and more than 80 species of this insect have been recorded in Uttarakhand.
- In addition, stem borer and leaf folder in rice and small millets, hairy caterpillar and sucking bug in soybean, leaf miner in garden pea, pod borer in pea and gram, fruit borer in tomato, blister beetle in beans and pigeon pea are other major pests.
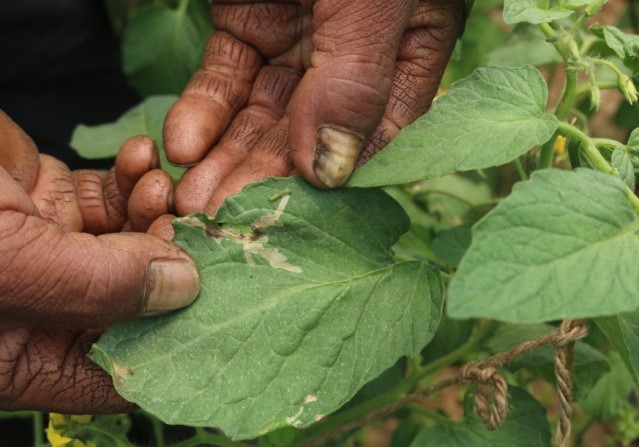
- Tuta absoluta, one of the serious pests of tomato causing extensive damage in many countries, was noticed in Uttarakhand hills during May 2018 in tomato grown under polyhouses (Bhagartola, Almora a MGMG village of ICAR-VPKAS). The farmers of the area were made aware about the identification of the pest and the potential damage. Severely infested polyhouses were sprayed with the insecticide, chlorantraniliprole @ 0.3 ml/l. Later on it was also observed from Dhari village of Nainital district
 |
 |
Crop Loss Assessment
Losses caused by major diseases and insects to important crops vary from slight to severe depending on the crop/variety and prevailing climatic conditions. Major pests, like blast and stem borer caused up to 65% and 52% losses, respectively in rice, stripe disease up to 72% in barley, white rot up to 58% in pea, buck eye rot up to 80% in tomato, anthracnose and frog eye leaf spot (combined) up to 40% in soybean and white grub up to 80% in rainfed rice.
Major Achievements
Resistant sources
The resistant genotypes were identified in various station, national and international nurseries in different crops. Artificial epiphytotics for blast in rice, turcicum blight in maize, rusts, loose smut and hill bunt in wheat are created to screen genotypes and advanced breeding lines thoroughly. Over the years, these evaluations have helped in identification of suitable high yielding genotypes with resistance/tolerance to major diseases and resulted in release of the varieties.
Genetic Stocks Registered
VL 798 (Reg. No. INGR 03007, IC 296431) Wheat - an immune stock to hill bunt disease, VL 639 (Reg. No. INGR 03011, IC 296480) Wheat - a resistant stock to loose smut have been registered with NBPGR. VSR 8 (Reg. No. INGR06002, IC546941) Rice - a source of blast resistance have been registered with NBPGR, New Delhi.
Eco-friendly management of diseases
- Indigenous Trichoderma harzianum isolates either singly or in combinations, delivered as seed treatment, soil drenching and with fortified FYM, resulted in significant reduction in root rots of French bean and lentil, damping-off of cauliflower and white rot in pea.
- Three isolates of Trichoderma harzianum have been identified as effective sclerotial parasites. These isolates significantly reduced seedling rot and white rot of pea.
- Soil solarization along with incorporation of organic manures (FYM or poultry manure) prior to mulching, and seed treatment with Trichoderma isolates reduced damping-off in tomato.
- Bio-fumigation with brassicaceous plants such as broccoli and toria were found effective in reducing root rot of cauliflower.
- Soil and foliage application of composts and compost extracts prepared from poultry manure and Urtica sp. provided high suppression of Rhizoctonia root rot and angular leaf spot diseases of French bean.
- Organic amendments with Ageratum, Parthenium and Urtica parviflora were found effective and resulted in significant reduction in the root rot incidence of cauliflower.
- Effective management of diseases using plant part extracts such as Oxalis latifolia and Cannabis sativa extracts for hill bunt of wheat and walnut extract for stripe disease of barley was observed.
Management of Insects
- Melia azedarach (Batain) seed kernel extract 10% was found to be effective against sucking bugs of French bean and soybean. Batain powder is used for the management of cutworms in chilies. Chemical insecticide, flubendiamide is found effective against pink borer, Sesamia inferens in rice. Deltamethrin is effective against blister beetles in pigeon pea and indoxacarb against Spodoptera litura in chili and tomato.
- Diaretiella rapae is found to parasitize cabbage aphids, Brevicoryne brassicae to an extent of 8.4 to 12.6% in the field. Campoletis chlorideae is the major parasitoid of borer, Helicoverpa armigera in field conditions.
- VL White grub Beetle Trap-1, an efficient and eco-friendly light based insect trap is found very effective in attracting and trapping Scarabaeid beetles. Beetles were trapped from second fortnight of May to September with a peak period of July. Anomala dimidiata is the predominant species followed by Holotrichia longipennis and H. seticollis.
- The microbial pathogens associated with diseased white grubs have been isolated and tested against white grubs. A bacterium, Bacillus cereus strain WGPSB2 is found very effective against white grubs and thus mass multiplied, formulated in talc and used in white grub management. It is recommended to mix the talc based bacterial formulation in farmyard manure and subsequently in the fields.
Development /Standardization of Mushroom Production Technology
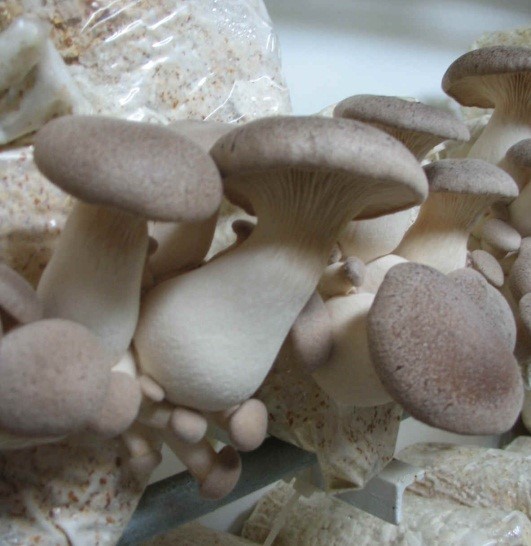
- Enhanced yield of Pleurotus eryngii (210.0/300 g dry substrate with BE 70%) was obtained using spent mushroom compost as casing overlay
 |
 |
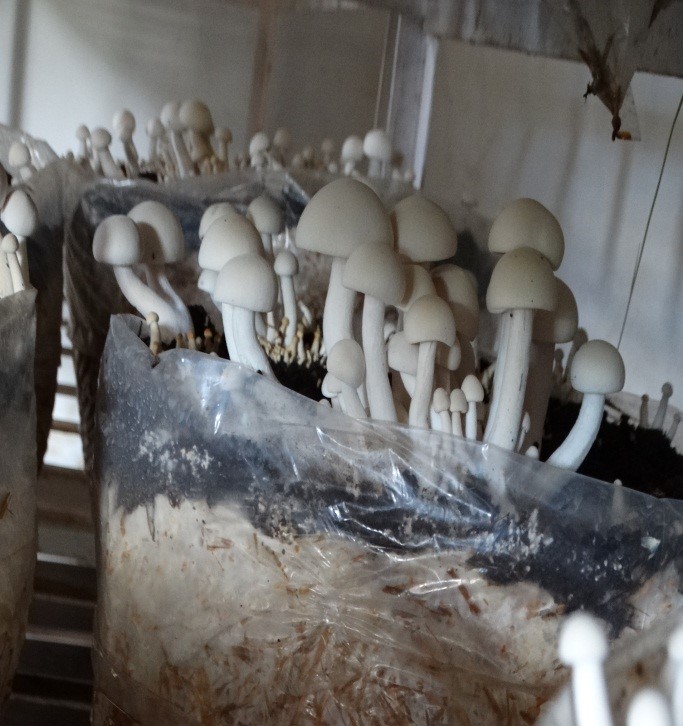
- A tropical mushroom Macrocybe gigantea was cultivated using wheat straw as substrate. The biological efficiency of mushroom was 70%.


Facility available
- Isolation, identification and maintenance of plant pathogens/insect pathogens.
- Artificial phenotyping for resistance to rice blast pathogens.
- Facility for mass production of important insects and bio-control agents viz. insect predators and pathogens like Trichoderma spp., Bacillus cereus.
- Extraction and isolation of insect pheromones/ volatiles through Air Entrainment.
- Spawn (mushroom seed) production of different edible mushroom species viz. Agaricus bisporus, Pleurotus sajor-caju, Pleurotus florida, Hypsizygus ulmarius, Macrocybe gigantea.
- Compost preparation using short method of composting for button mushroom production.
List of Equipments:
- Fluorescent microscope
- Horizontal electrophoresis unit
- Vertical electrophoresis unit
- PCR Thermocycler
- Insect growth chamber
- BOD Incubator
- Incubator shaker
- Laminar air flow
- Research Microscopes
- Compound Microscope
- Deep freezer (-200C)
- Refrigerators
- Double distillation unit
- Horizontal autoclave
- Vertical autoclave
- Electronic weighing balance
- Hot air-oven
- Micro oven
- Refrigerated centrifuge


























